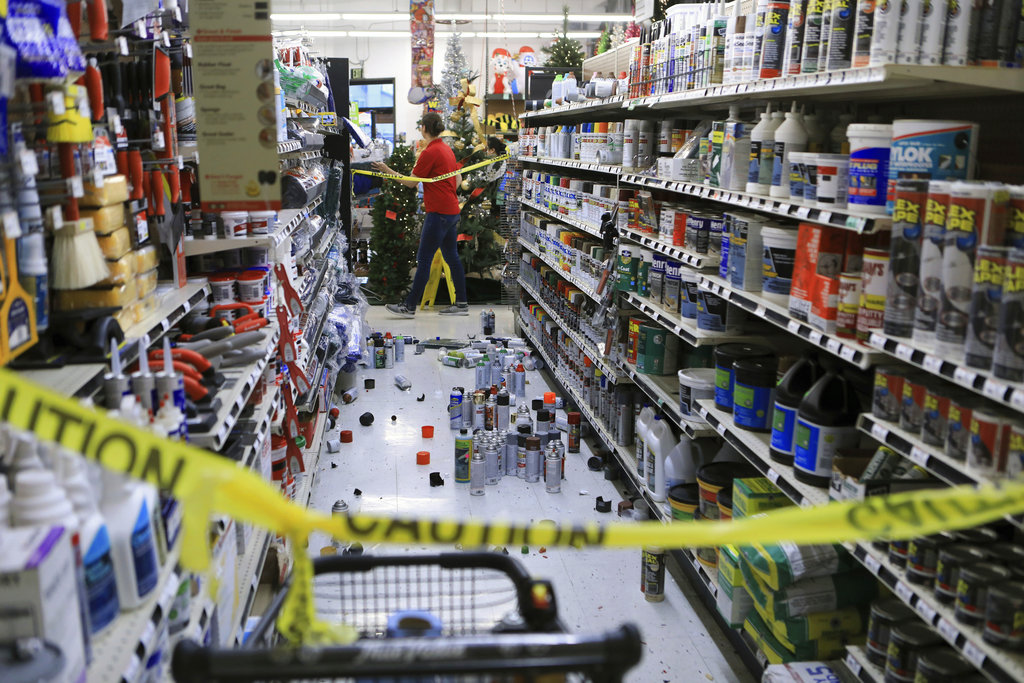


To get ShakeAlert-powered alerts on your phone, please visit: /faqs/how-do-i-sign-shakealertr-earthquake-early-warning-system Who is this website for? These automated actions could include slowing trains, closing water valves, turning on backup generators, issuing public announcements, and many others.įor general information about ShakeAlert, please visit: /ShakeAlert The largest was a magnitude 5.9, eight minutes after the magnitude 8.2. since a magnitude 8.7 quake in the Aleutians in 1965. The USGS works with licensed technical partners who use USGS-issued ShakeAlert Messages to alert people to take a protective action or to trigger automated actions. The Alaska Earthquake Center reported 14 aftershocks of magnitude 4 or larger in the first two hours after the quake. The Alaska Earthquake Center said on its website that it was the largest quake in the U.S. Here in Alaska, though, tsunamis generated by nearby earthquakes represent near-field hazards. Historically, tsunamis generated by earthquakes in Alaska have caused damage and loss of life along the West Coast and across the Pacific. The purpose of the system is to reduce the impact of earthquakes and save lives and property. Coastal Alaska communities live with the most serious tsunami risk in the United States. Geological Survey, detects significant earthquakes quickly enough so that alerts can be delivered to people and automated systems potentially seconds before shaking arrives. All rights reserved.The ShakeAlert® Earthquake Early Warning System, managed by the U.S. That would be a highly destructive, and damaging, and potentially deadly event.”Ĭopyright 2021 KTVF.
They don’t happen very often, perhaps not in our lifetime, perhaps next month - and an earthquake of that size today, we would be talking about very different things right now had that earthquake occurred. However, we know that the Salcha Seismic Zone is capable of earthquakes like that. Fairbanks was a different place of course in 1937. On average, Alaska experiences half a dozen magnitude 6 or greater earthquakes per year. New Zealands 2011 M6.3 Christchurch earthquake, for example, claimed 185 lives and caused billions of dollars in damage. “That’s an earthquake that had tremendous impacts on the surface of the earth - you know, big cracks, fault lines, it had violent shaking across the Fairbanks region. However, moderate-to-strong earthquakes happening near cities and towns pose serious dangers to people and infrastructure. One of the reasons we pay attention to this area, and that it’s on the radar so to speak, is that it’s not far from the location of the 1937 earthquake which was in excess of magnitude seven” West continued. The Castle Mountain Fault, which passes 25 miles (40 km) north of Anchorage, exhibits geological evidence of Holocene offsets and generated the 1984 M5.6 Sutton Earthquake. So I think it’s safe to say that we’ll be keeping an eye on that area over the next few months.”Īnd along with July’s earthquake, historically, there is precedent for much larger quakes in the same area. The chart shows how much earthquake activity we are detecting at different volcanoes relative to their background levels. The April 1933 M6.9 earthquake, which caused considerable damage in Anchorage, appears to have occurred on such a structure.

But it does catch our attention that we’ve had two of them, and this is an area where we know that historically, much larger earthquakes are possible.
#Alaska quake center series#
“Two earthquakes do not create, you know, a sequence or series or something.

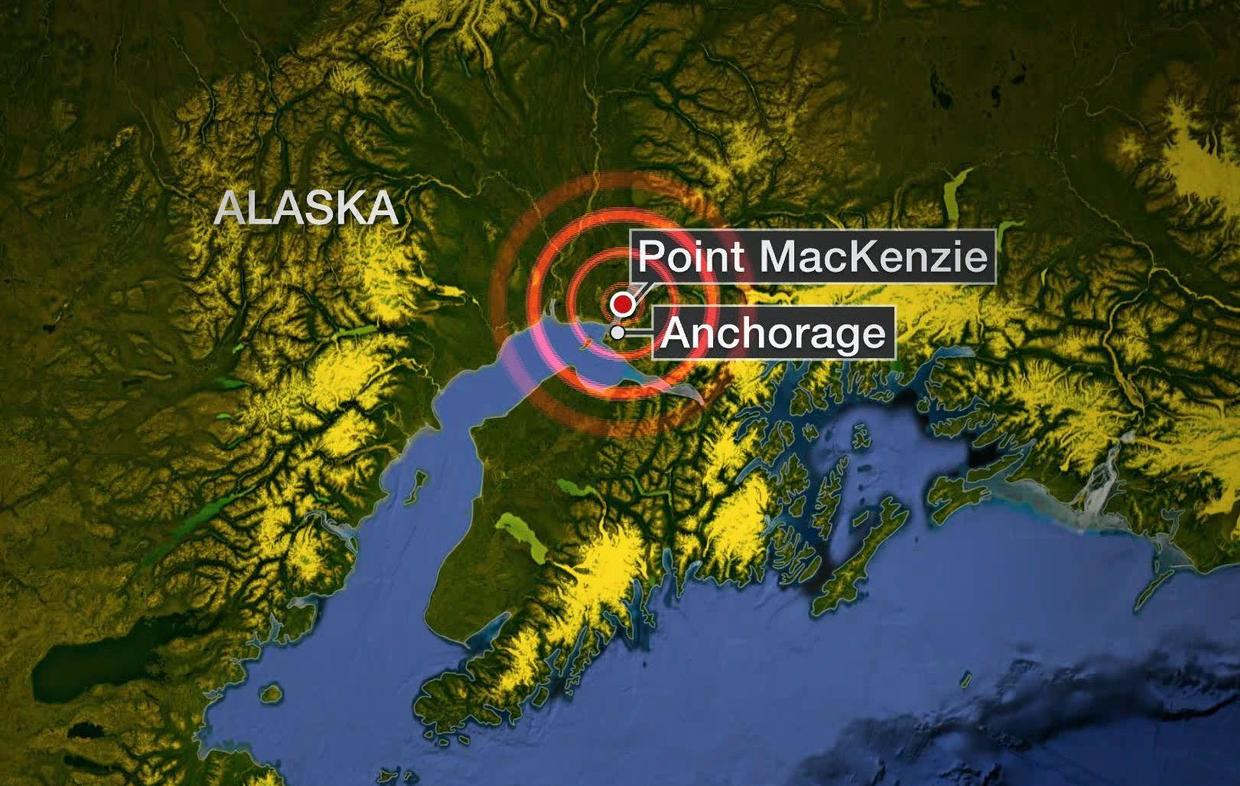
“One of the things that has our attention, is that this earthquake occurred more or less in the same place as a almost as large earthquake back in July,” West said. There’s a geologic feature of some sort that is prone to creating these quakes.”īut what caught the eye of the Alaska Earthquake center was this quake’s proximity to another. If you take the location of all the historical earthquakes, there’s a feature there. They, rather, fall along a very well defined delineation. “We call it that because there’s a history of earthquakes here and they are not randomly scattered around. “The location of this earthquake is not a surprise, it happened in an area that we refer to loosely as the Salcha Seismic Zone,” West explained.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
